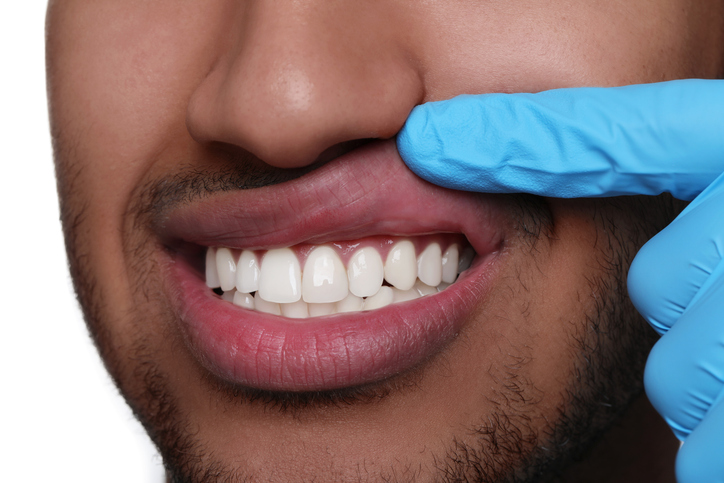
Common Causes and Risk Factors
Several factors contribute to the development of gum disease. Poor oral hygiene, such as infrequent brushing and flossing, allows plaque—a sticky film of bacteria—to build up on your teeth and gums. Other risk factors include smoking, hormonal changes in women, diabetes, certain illnesses and medications, and genetic susceptibility. It’s essential to understand these causes to take proactive steps in preventing gum disease.
Importance of Early Detection and Treatment
Early detection and treatment of gum disease are crucial for maintaining your oral health. Gingivitis, the initial stage, can be reversed with professional cleaning and proper oral hygiene. However, if it progresses to periodontitis, more intensive treatments are necessary. By addressing gum disease early, you can prevent the loss of teeth and reduce the risk of other health complications associated with periodontal disease, such as heart disease and diabetes.
Recognizing the Symptoms of Gum Disease
Early Signs to Watch For
Recognizing the early signs of gum disease can help you seek treatment before it becomes severe. Common symptoms include red, swollen, and tender gums, bleeding while brushing or flossing, persistent bad breath, and receding gums. If you notice any of these symptoms, it’s essential to schedule an appointment with Dr. Sams for an evaluation.
Progression of Gum Disease: From Gingivitis to Periodontitis
Gum disease progresses in stages, starting with gingivitis. During this stage, you may notice mild symptoms like gum redness and bleeding. Without intervention, gingivitis can advance to periodontitis. In periodontitis, the inner layer of the gum and bone pull away from the teeth, forming pockets that become infected. As the disease progresses, these pockets deepen, and the supporting bone and connective tissue are destroyed, potentially leading to tooth loss.
Why Ignoring Symptoms Can Lead to Serious Health Issues
Ignoring the symptoms of gum disease can have serious consequences for your oral and overall health. Advanced gum disease can result in tooth loss and may contribute to systemic conditions like cardiovascular disease, respiratory infections, and complications in diabetes. By addressing gum disease promptly, you can protect not only your smile but also your general well-being.
Treatment Options for Gum Disease
Non-Surgical Treatments: Scaling and Root Planing
One of the primary non-surgical treatments for gum disease is scaling and root planing. This deep cleaning procedure involves removing plaque and tartar from above and below the gumline. Our team uses specialized tools to clean the tooth surfaces and roots, helping to reduce bacterial buildup and promote healing. This treatment is often sufficient for managing mild to moderate cases of gum disease.
Surgical Interventions: Flap Surgery, Bone Grafts, and Tissue Grafts
In more advanced cases of gum disease, surgical interventions may be necessary. Flap surgery, or pocket reduction surgery, involves lifting back the gums to remove tartar deposits and then securing the gums back in place. Bone grafts are used to regenerate bone lost due to periodontal disease, while tissue grafts can help restore gum tissue that has receded. These surgical options aim to rebuild and stabilize the supporting structures of your teeth.
The Role of Medications and Antibiotics in Treating Gum Disease
Medications and antibiotics play a vital role in the treatment of gum disease. Antimicrobial mouth rinses and antibiotic gels can be applied to the gums or placed in periodontal pockets to control bacterial infection. In some cases, oral antibiotics may be prescribed to eliminate infection. These medications are typically used in conjunction with other treatments to enhance their effectiveness and support the healing process.
Home Care and Lifestyle Changes
Daily Oral Hygiene Practices to Combat Gum Disease
Maintaining excellent oral hygiene is essential for combating gum disease. Brush your teeth at least twice a day with fluoride toothpaste, and don’t forget to clean along the gumline. Floss daily to remove plaque and food particles between your teeth where your toothbrush can’t reach. Using an antiseptic mouthwash can also help reduce bacteria in your mouth. These practices are the first line of defense against gum disease and play a crucial role in preventing its recurrence.
Dietary Adjustments for Better Oral Health
Your diet significantly impacts your oral health. Consuming a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals supports healthy gums and teeth. Focus on foods high in vitamin C, such as citrus fruits and leafy greens, which help strengthen gum tissue. Avoid sugary and acidic foods and beverages that can contribute to plaque buildup and gum inflammation. Staying hydrated by drinking plenty of water also aids in maintaining good oral health.
How Smoking and Other Habits Impact Gum Health
Smoking is one of the most significant risk factors for gum disease. It impairs blood flow to the gums, making it harder for your body to fight infections and heal properly. Quitting smoking can significantly improve your gum health and overall well-being. Additionally, habits like teeth grinding (bruxism) can exacerbate gum problems and should be addressed with the help of our team. Adopting healthy habits and eliminating harmful ones can make a significant difference in your oral health.
Maintaining Oral Health Post-Treatment
Regular Dental Check-Ups and Professional Cleanings
Regular dental check-ups and professional cleanings are essential for maintaining your oral health after gum disease treatment. Our team will monitor your condition, ensuring that any signs of recurrence are detected early. Professional cleanings remove plaque and tartar that regular brushing and flossing might miss, keeping your gums healthy. Aim to visit us at least twice a year or more frequently if recommended by Dr. Sams.
Long-Term Strategies for Preventing Recurrence
Preventing the recurrence of gum disease requires a commitment to long-term oral care strategies. Continue practicing excellent oral hygiene at home, including brushing, flossing, and using mouthwash. Follow a balanced diet and stay hydrated to support your gum health. If you have a history of gum disease, consider using interdental brushes or water flossers to enhance your cleaning routine. We can provide personalized recommendations to help you maintain your oral health.
The Connection Between Oral Health and Overall Well-Being
Your oral health is closely linked to your overall well-being. Studies have shown that gum disease is associated with various systemic conditions, including heart disease, diabetes, and respiratory infections. By maintaining healthy gums, you’re not only preserving your smile but also supporting your general health. Regular dental visits and good oral hygiene practices are integral to a healthy lifestyle.
In conclusion, addressing gum disease through early detection, appropriate treatment, and ongoing care is vital for maintaining both your oral and overall health. At Implant & Perio Center of Kansas, Dr. Sams and are dedicated team are committed to helping you achieve and maintain a healthy smile. If you have any concerns about gum disease or need to schedule an appointment, don’t hesitate to contact us. Together, we can ensure your oral health remains in optimal condition.
